At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is Plant Biosynthesis?
Plant biosynthesis is the collection of natural processes that plants undergo to convert inorganic mineral elements such as potassium and nitrogen in soil along with elements in water and air into nutrients, using energy derived initially from sunlight. These processes are broken down into three basic categories for plants, which include photosynthesis, respiration, and chemical synthesis. Like animals and other living organisms such as bacteria, plants rely on the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to survive. They also synthesize and break down many of the same compounds in plant biosynthesis that animals do, including amino acids, lipids, and carbohydrates.
Understanding the key processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in plants is the first step towards understanding biosynthesis in plants overall. Photosynthesis is a process that takes the energy from visible light in specific wavelengths and stores it in sugar molecules in plants through the use of choloroplasts. Chloroplasts are small organelles within plant cells that contain chlorophyll, a green compound that gives plants their color and is used in synthesizing carbohydrates such as sugar.

Plant biosynthesis uses three different types of pigments to maximize its absorption of light. The pigment chlorophyll a absorbs light most strongly around the 430 nanometer wavelength, which is largely blue in color, and chlorophyll b absorbs light around a 470 nanometer wavelength which is true green. Another pigment produced by some plants is carotenoid, which absorbs light in the yellow to orange range of the visible spectrum from 500 nanometer wavelengths or greater.

Plant respiration is also a key feature of how plants function to take in carbon dioxide and remove oxygen as a waste gas, but they do not breathe these gasses in and out as animals do. The process of respiration in plant biosynthesis involves plants allowing air to diffuse into their external cellular structure, where these combined gasses are then transported by water to internal cellular membranes. The energy for respiration comes from stored glucose created during photosynthesis. Plants break down glucose for energy just as animals do, and are rather efficient at it with a net energy gain of 22% to 38%. This is superior to many forms of modern human technology such as the automobile, which is less than 25% efficient at converting gasoline to energy for motion.

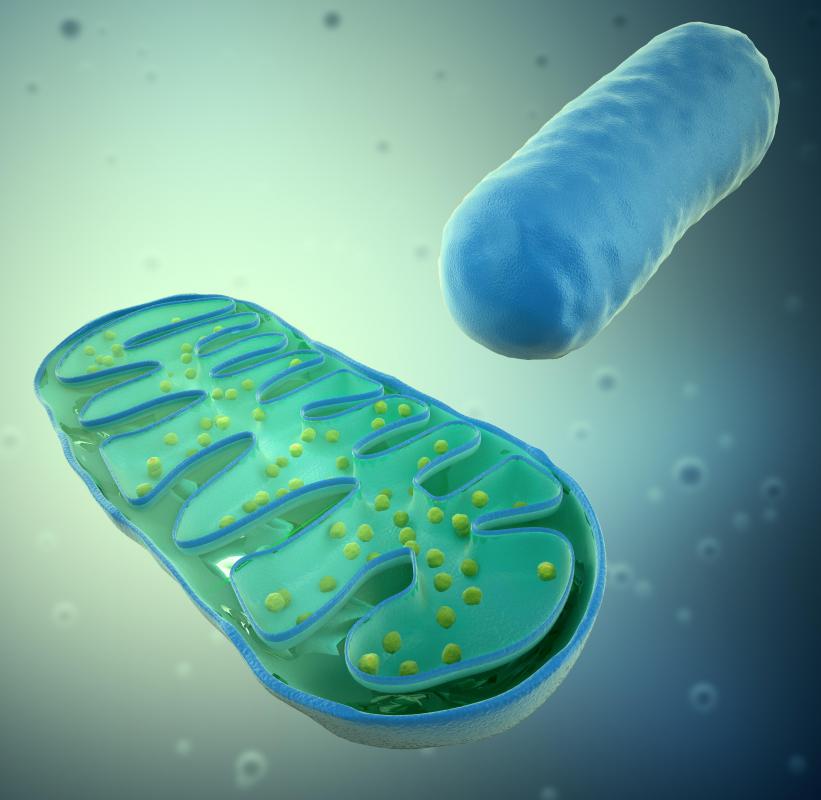
The energy production process in plant biosynthesis is based on the same chemical reaction that all animals use to generate energy. Plants utilize molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to both store and release energy as ATP is both built up chemically and broken down by mitochondria in plant cells. The difference between plants and animals in this process is that the waste products of energy production for plants are also glucose, oxygen, and water, all of which are essential compounds that animals rely on for survival.

Plant metabolism of other chemicals can be extremely complex, and science is intricately involved in studying biosynthesis pathways in plants due to the numerous types of useful organic compounds that plants produce. Plant enzymes are known as of 2011 to synthesize over 200,000 different types of chemicals, many of which can be harvested for use in food products and medicines. Most commercially useful compounds produced by plant biosynthesis cannot yet be made by artificial means in laboratory settings, however, so the plants themselves must be grown to harvest the chemicals. Research into plant biosynthesis as of 2011 focuses on the actual methodology that a plant uses to create a compound, and, once this is thoroughly understood, cell cultures of the plant can be grown in large numbers to produce the chemical commercially.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is plant biosynthesis?
Plant biosynthesis is the process by which plants produce complex organic compounds from simple substances. This occurs primarily through photosynthesis, where sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. These organic compounds serve as building blocks for plant growth and development, enabling them to create everything from structural components to defensive chemicals.
How does photosynthesis contribute to plant biosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the cornerstone of plant biosynthesis. It provides the energy and basic carbon structures needed for synthesizing a wide array of organic molecules. During photosynthesis, plants capture sunlight using chlorophyll and convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which is then used to generate other organic compounds essential for the plant's survival and growth.
Are there different types of biosynthesis in plants?
Yes, plants perform various types of biosynthesis. Primary biosynthesis involves the formation of essential molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Secondary biosynthesis produces specialized compounds like alkaloids, terpenoids, and flavonoids, which can aid in defense, pollinator attraction, and UV protection. These pathways are crucial for plant adaptation and ecological interactions.
What role do enzymes play in plant biosynthesis?
Enzymes are vital catalysts in plant biosynthesis, speeding up chemical reactions that would otherwise occur too slowly to sustain life. They facilitate the conversion of substrates into products through metabolic pathways, ensuring efficiency and specificity in the synthesis of complex molecules. Enzymes also regulate the rate of these reactions, allowing plants to respond to environmental changes.
Can plant biosynthesis impact the environment?
Plant biosynthesis has a profound impact on the environment. Through photosynthesis, plants act as carbon sinks, reducing atmospheric CO2 levels, which is crucial for mitigating climate change. Additionally, the oxygen released during photosynthesis is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms. Plants also contribute to soil health by adding organic matter and supporting diverse ecosystems.
How does plant biosynthesis affect human life?
Plant biosynthesis is essential for human life, providing the basis for our food supply through the production of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Medicinal compounds derived from plants are also the result of biosynthetic pathways, leading to the development of numerous drugs. Furthermore, plants produce oxygen and help regulate the Earth's climate, both critical for human survival.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments