At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Marine Biology?
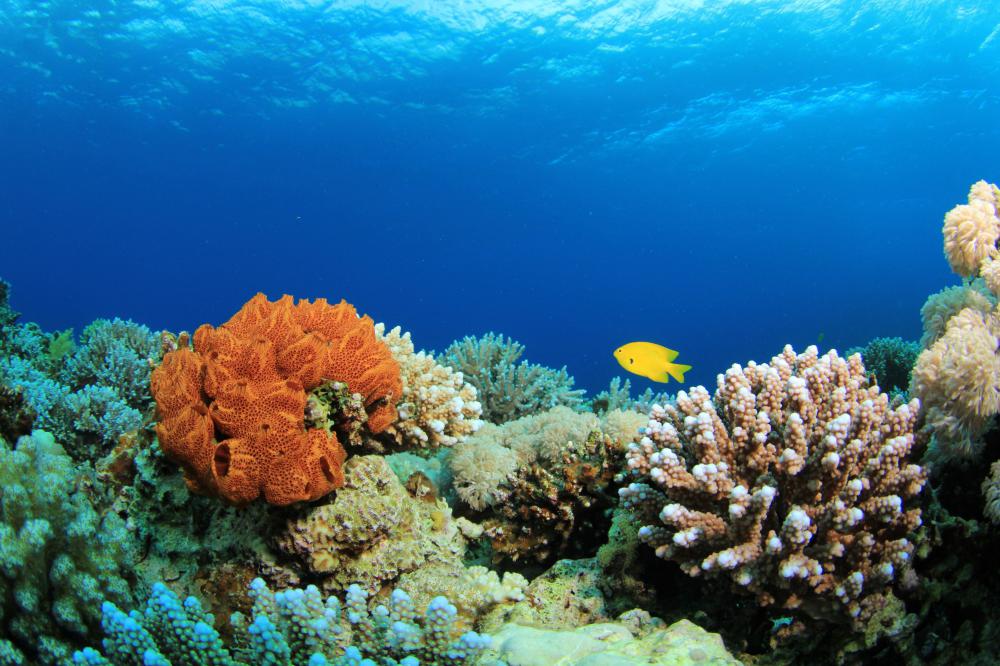
Marine biology is the study of life forms living in saltwater, and therefore, usually an ocean environment. Studies in this field may include the analysis of plants, fish, microscopic organisms and marine mammals. Marine biologists may also study the whole of an ocean ecosystem, or a specific type of life form and how it interacts with its habitat.
People who work in marine biology may do so in the field or analyze data gathered from ocean sites. It can be comparative in nature, and might include an analysis of similar bacteria existing in several different oceans. Alternately, it can be specific to just one species or location.

Other forms of science, particularly climatology as it affects ocean life forms, oceanography, and animal behavior, are connected to the field. While some marine biologists may study the biological structure of an animal, others might study how it behaves.
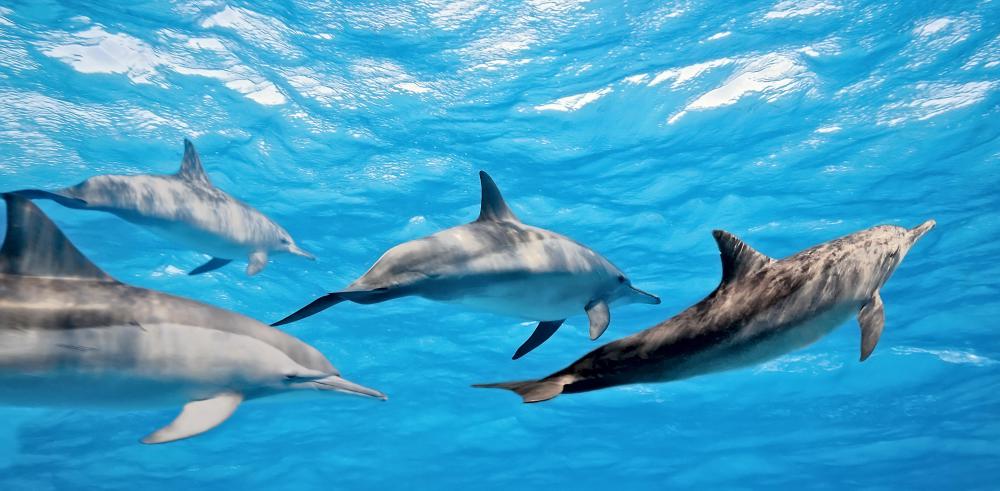
Often people think of marine biology as only the study of marine mammals, like whales, dolphins or seals. This actually represents just a small portion of the scientific field. There are relatively few marine mammals as compared to vast numbers of species of fish, plants, and single-celled organisms in ocean environments. Understanding the mechanism and interactions of these less glamorous species tend to shed light on important facts about the marine mammals that do exist.

Marine biology may also involve a certain amount of activism. Many scientists who consider themselves marine biologists have amassed a great deal of additional scientific education. This is because the field must be understood in the context of other sciences. In addition, if one wants to become engaged in protecting the ecosystems of the ocean, writing and speaking skills are immensely important.

Not everyone who studies marine biology does so at the ocean, and there are a number of sites of study in landlocked states or countries. This is because oceans and their lifeforms have an effect on all areas. Prehistoric biology may also evaluate the specimens of extinct ocean life forms that are present in areas where no saltwater bodies still exist.

Experts in this field may also the study how the organisms in the ocean may benefit human life. The oceans’ many different life forms may hold potential health benefits, give keys to developing beneficial medications, or help scientists determine how best to protect earthbound life forms.
Some find marine biology particularly appealing because so many of the ocean’s species remain unknown. There are ocean areas that people still cannot access because of temperature or depth. The ocean is a frontier that humans have not yet breached, so people in the field regularly have the opportunity to be a part of earth and life science studies that lead to brand new discoveries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is marine biology?
Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine bodies of water. It encompasses a diverse range of topics, including the behavior, physiology, and ecology of marine species, as well as the health of marine ecosystems and the impact of human activity on the oceans.
Why is marine biology important?
Marine biology is crucial for understanding the health of our planet, as oceans cover more than 70% of the Earth's surface and are home to a vast array of biodiversity. According to the World Register of Marine Species, there are over 240,000 known marine species, and this knowledge helps us protect marine environments and manage resources sustainably.
What do marine biologists do?
Marine biologists study life in the oceans, from microscopic plankton to the largest whales. Their work can involve field research, such as collecting samples and observing behaviors, laboratory experiments, data analysis, and creating models to predict future changes. They also play a role in conservation and policy-making to protect marine ecosystems.
What are some subfields of marine biology?
Marine biology includes several specialized subfields, such as marine ecology, fisheries biology, marine conservation, phycology (study of algae), and marine biotechnology. Each area focuses on different aspects of marine life and contributes to our overall understanding of marine ecosystems and how to preserve them.
How does marine biology affect human society?
Marine biology has a direct impact on human society by informing sustainable fishing practices, contributing to medical advances through marine biotechnology, and aiding in climate change research, as oceans play a key role in regulating the Earth's climate. It also influences marine policy and conservation efforts to ensure the health of our oceans for future generations.
What are the biggest threats to marine ecosystems?
The biggest threats to marine ecosystems include overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and ocean acidification. These threats can lead to loss of biodiversity and disruption of marine food webs. Efforts by marine biologists to monitor and mitigate these threats are vital for the preservation of marine life and the overall health of our planet.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
Why are marine biologist so looked down upon? Why does the government take the research that exposes the truth? Why is the government afraid of something?
For those interested in prehistoric marine biology, the Seazoria Discovery offers new insight into the largest advanced biological structures ever discovered. See information and photos of biological remains from the Seazoria marine ecosystem. Seazoria Marine Biology and Paleontology represent a new scientific frontier in life sciences.
@ Anon18618- You also have the option of pursuing a degree in Oceanography. Oceanography and marine biology are very closely related. The career path for both fields is similar, except oceanography is a little more geological and physical sciences oriented. Oceanographers deal more with the relationship between ocean organism and their physical environment, while marine biologists focus more on the chemical and physical properties of ocean organisms.
@ Anon18618- I assume that you are talking about the Advanced Level GCE that Commonwealth and former Commonwealth states of the UK award. I am not that familiar with how the system works, but I can tell you what it takes to become a marine biologist in the States.
TO work in specialized fields in the United States it is often required that you obtain a BS in Biological sciences, Molecular biology, or Biochemistry. Once you move on to an advanced degree program, you begin your specialization. To perform independent research a PhD or its equivalent is often required, with a post-doc research background preferred. So to reach your goal of working in marine biology, take courses in biology, chemistry, mathematics, and other natural sciences. I hope this helps to answer your question.
After which educational degree one would start studying on marine biology?
What subjects do I need to study on my A' Level to proceed to marine biology? Can anyone having science subjects study on this topic? Or are there any exceptions?
Post your comments