At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Causes the Sky to Look Blue?
One of the eternal questions long thought unanswerable is what causes the sky to look blue. Modern science and the understanding of light waves have provided an answer, although many false answers are still popular. What causes the sky to look blue is the result of electromagnetic scattering, using the light from the sun and the particles of Earth’s atmosphere.
To understand what causes the sky to look blue you must understand how light waves work. A light wave is a vibrating field of energy that travels in waves. The distance from one wave to the next is called the wavelength, and determines the color of the light. Light from the sun contains all different colors; all blending together to form a white light that travels in a straight line until it bumps into anything. Depending on the object it bumps into, the light can be broken into different lengths of light waves. The shortest light waves correspond to blue and violet colors, which also have the most contained energy and the highest frequency.

When a light wave hits a gas particle, such as those that make up the atmosphere surrounding earth, the particle can absorb some of the energy of the wave. Whatever energy the particle absorbs, it radiates or reflects. Because they have the highest frequency, blue light waves are much more often absorbed than their slower, less energetic companions.

Rayleigh scattering, a process named after the English scientist who discovered it, describes what causes the sky to look blue. Because of microscopic textures in the surfaces of the atmosphere’s particles, the blue absorbed light doesn’t just radiate or reflect in one direction, it shoots off in all sorts of directions. As you look at the sky, you are seeing the scattered light as it bounces all around the atmosphere.

Rayleigh scattering also describes why the sky seems to lighten in color toward the horizon. Because you are looking at sky much farther away, the light waves are passing through more air to get to you. The farther away you look, the less concentrated the scattering becomes, causing lighter blue shades near the edge of the horizon.
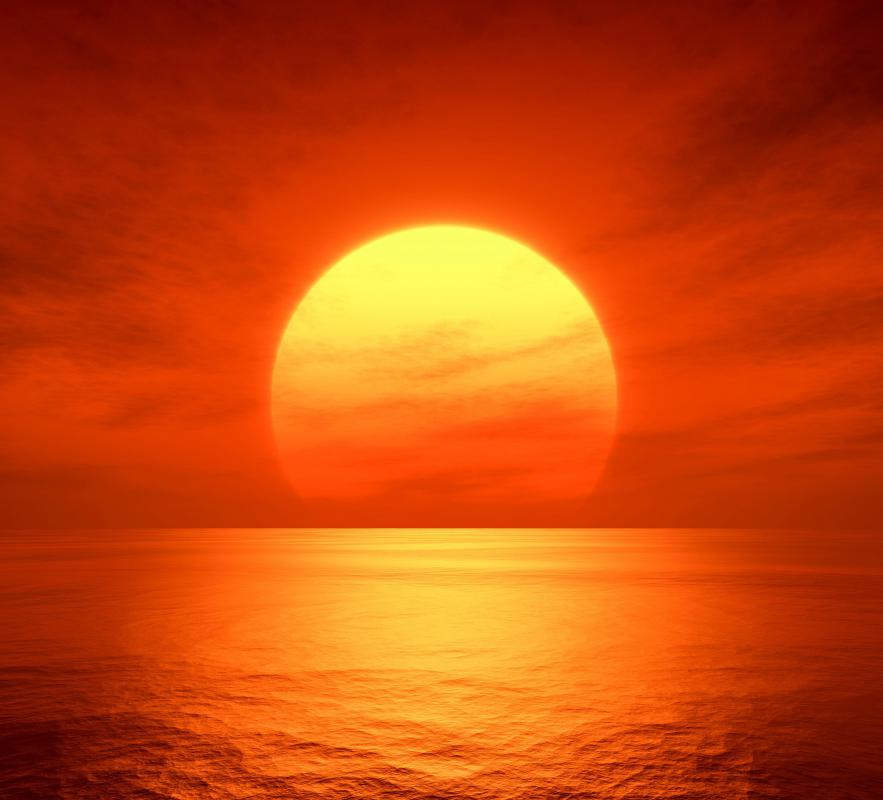
If you are wondering why, at sunrise or sunset, the sky turns red and orange, this is also a scattering process. When the sun is near the horizon, it must pass through much more atmosphere. As it does, the longer light waves that pass through thinner layers of the atmosphere are the only waves not to be completely diffused by the scattering. The longer light waves make up orange and red colors, so that is the light that becomes visible at sunrise and sunset.
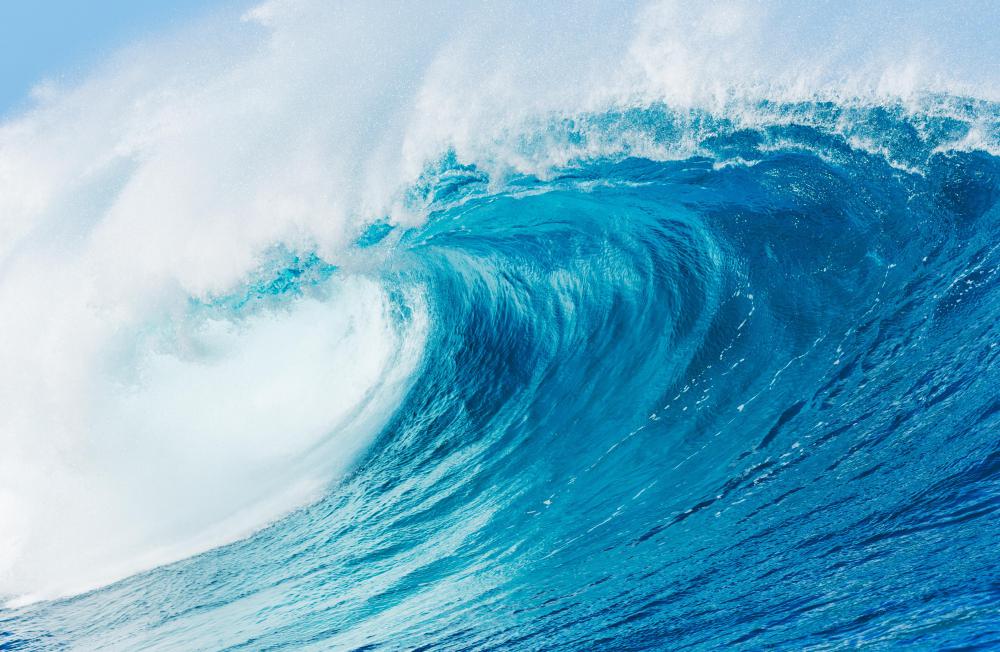
Popular false explanations suggest that the sky is blue because the light reflects off of the blue oceans. In fact, it works the other way around. What causes the ocean to look blue is the same thing that causes the sky to look blue. The ocean is reflecting the color of the sky, so if the sky is scattered blue light, particles in the ocean will receive and scatter mostly blue light.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the sky blue instead of another color?
The sky appears blue due to a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. As sunlight enters Earth's atmosphere, it collides with gas molecules. These collisions scatter shorter blue wavelengths more than other colors because they travel as smaller, shorter waves. This scattering causes the blue hue to dominate the sky we see.
Does the sky appear blue at all times of the day?
No, the sky does not appear blue at all times. During sunrise and sunset, the sky can take on shades of red, orange, and pink. This is because the sun's light passes through more atmosphere at these angles, scattering shorter blue wavelengths out of the line of sight and allowing longer red wavelengths to be seen.
Can pollution affect the color of the sky?
Yes, pollution can affect the sky's color. Particulates and pollutants in the atmosphere can scatter and absorb sunlight differently, sometimes leading to a duller or even grayish sky. In some cases, pollution can enhance reds and oranges during sunrise and sunset, according to the Environmental Protection Agency.
Is the sky blue on other planets as well?
The color of the sky on other planets depends on their atmospheres' composition. For instance, Mars has a thin atmosphere filled with dust, making its sky appear reddish. Meanwhile, the sky on Neptune is blue due to the presence of methane, which absorbs red light and scatters blue light, similar to Earth's Rayleigh scattering.
Why does the sky not look blue to astronauts in space?
Astronauts in space see a black sky instead of blue because there is no atmosphere to scatter sunlight. Without an atmosphere, like on Earth, there are no air molecules to cause Rayleigh scattering, which is responsible for the blue sky we see from the planet's surface.
How do weather conditions influence the color of the sky?
Weather conditions greatly influence sky color. A clear, blue sky is typically seen when the atmosphere is free of pollutants and large particles. However, when it's overcast, clouds scatter and reflect all wavelengths of light, giving the sky a white or gray appearance. Additionally, certain weather phenomena can cause unique colors, such as the greenish tint sometimes observed during severe thunderstorms.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
The sky is blue because it's a reflection of the sea.
Post your comments