At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
In Meteorology, what is an Inversion?
An inversion is a situation in which the layers of the atmosphere do not act normally, inhibiting normal weather processes and often trapping smog, smoke, and clouds close to the ground. The most common form of inversion is a temperature inversion, although inversions can take other forms as well. Essentially, an inversion can be thought of as a flip in the natural order of things, suppressing convection and other processes which allow air to cycle across the earth.
In normal conditions, hot air close to the ground slowly rises upwards, pushing through a layer of cooler air. When a temperature inversion occurs, cooler air gathers near the ground, with a layer of hot air pressing down on top of it. This forces clouds, smog, and pollution to be trapped near the ground, because they cannot waft upwards, and a temperature inversion can sometimes break explosively, with severe thunderstorms or tornadoes.

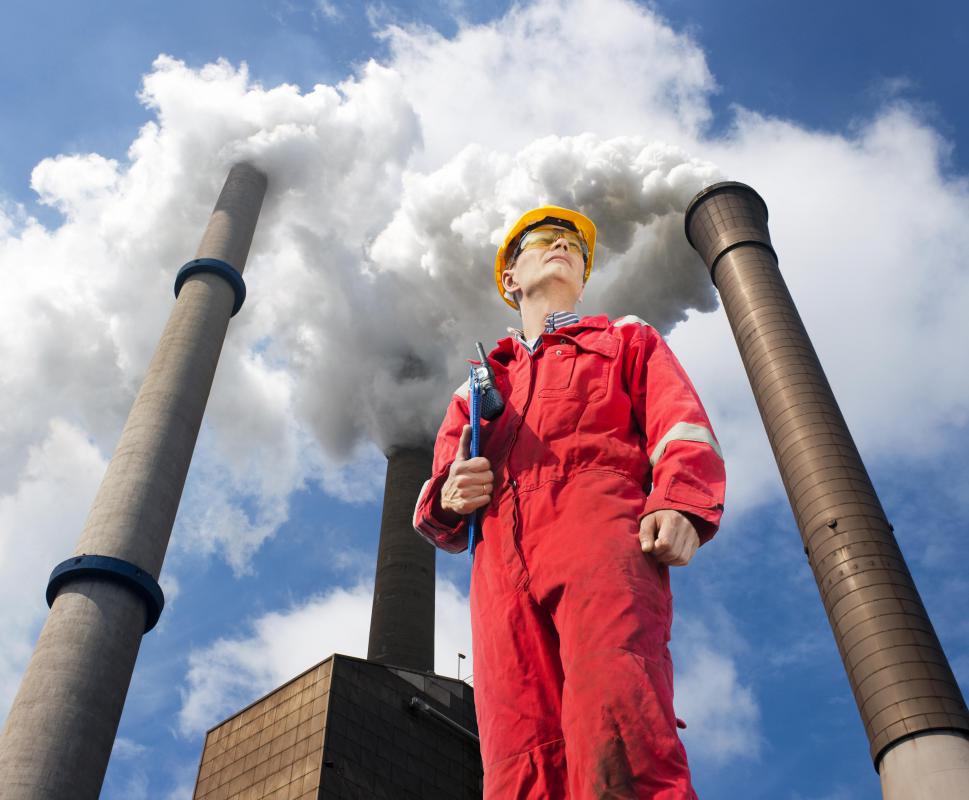
One classic form of temperature inversion is the marine inversion, caused by cool air from the surface of the ocean being pushed onto shore. Marine inversions explain why many coastlines around the world are foggy. Inversions also commonly appear in valleys, where warm air presses down on cooler air in the valley. Since many urban areas are in valleys or near the ocean, they often suffer from extreme pollution made worse by inversions.

A weather inversion does not just impact the weather in the surrounding area. Inversions can also affect human health, as in the case of an inversion which traps pollution, and they can also impair visibility by forcing heavy cloud cover close to the ground. Inversions can also play funny tricks with radio signals and sounds; radio signals are often stronger during an inversion, for example, and the heavy fog characteristic of marine inversions can do peculiar things to noises, making them seem further or closer than they really are.

Inversions ultimately resolve themselves, sometimes quite abruptly, and sometimes they appear and disappear several times over the course of a day. In other instances, an inversion may hover for several days, often leading to concerns about air quality and potentially dangerous weather conditions.
Capping inversions, in which a layer of hot air traps a layer of cooler air, are notorious in the Midwest, because when the cap finally breaks, a huge amount of energy can be released, resulting in severe weather. The “cool” air in such inversions is often actually quite warm, so these inversions can feel very oppressive and tense until they finally disappear.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an inversion in meteorology?
An inversion in meteorology refers to a reversal of the normal temperature gradient in the atmosphere. Typically, air temperature decreases with altitude, but during an inversion, a layer of cooler air is trapped near the ground by a layer of warmer air above. This can lead to various weather phenomena, such as reduced air quality and fog formation.
How does an inversion affect weather and climate?
An inversion can significantly impact local weather by stabilizing the atmosphere, which suppresses cloud formation and can lead to clear skies. However, it can also trap pollutants and moisture, causing smog and persistent foggy conditions. Inversions can affect climate patterns by influencing local temperature distributions and potentially altering precipitation processes.
What causes atmospheric inversions to occur?
Atmospheric inversions can be caused by several factors. Radiational cooling of the Earth's surface overnight can lead to a ground inversion, while a warm air mass moving over a cooler one can create a subsidence inversion. Additionally, geographical features like valleys can enhance inversion conditions by trapping cool air in lower regions.
Are inversions more common in certain geographical locations?
Yes, inversions are more common in certain areas, particularly in valleys and basins where cool air can settle and become trapped by surrounding terrain. Cities with high pollution levels can also experience frequent inversions. For example, Salt Lake City in Utah is known for its temperature inversions during winter, which can lead to poor air quality.
Can inversions be predicted?
Meteorologists can predict inversions by analyzing weather patterns and atmospheric conditions. They use tools like satellite imagery, weather balloons, and computer models to forecast when and where an inversion might occur. Predicting inversions is crucial for air quality management and advising the public on potential health risks.
What are the environmental and health impacts of inversions?
Inversions can have significant environmental and health impacts by trapping pollutants near the surface, leading to poor air quality. This can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and contribute to cardiovascular problems. Environmentally, inversions can harm plant life by exposing vegetation to higher concentrations of pollutants and reducing the dispersion of greenhouse gases.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discussion Comments
Does an inversion often have a bad odor?
Post your comments